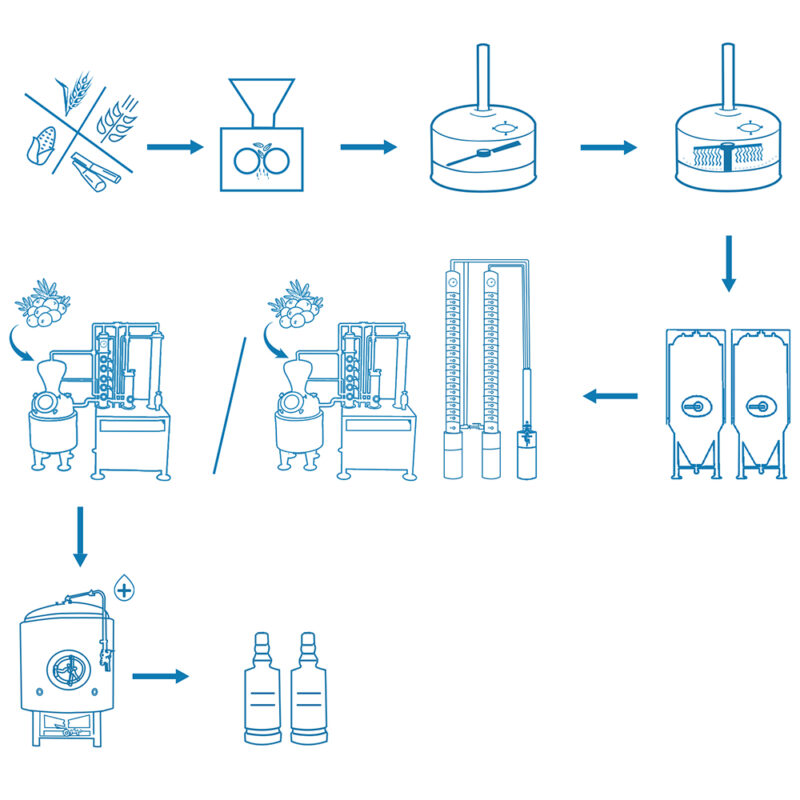
How to Distill Gin?
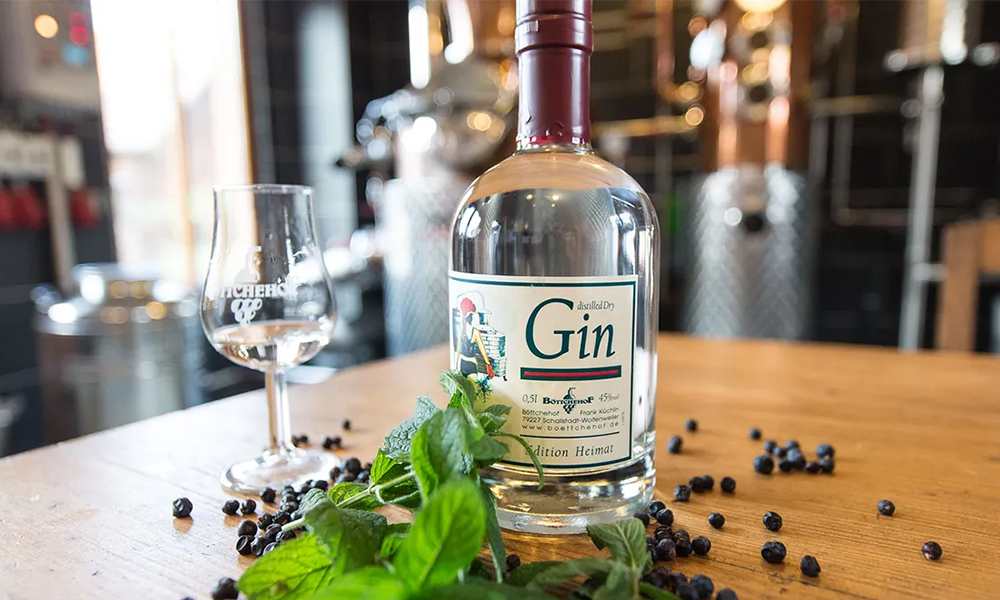
What is Gin?
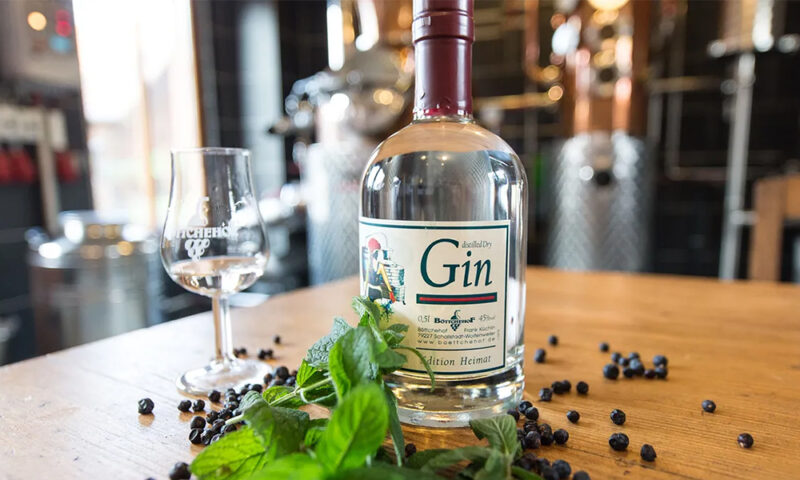
Gin is a type of spirit characterized by the flavor of juniper berries.When it comes to gin production, distillers begin with a neutral spirit and then add different botanical flavors and ingredients throughout the distillation process. For liquor to be classified as gin in the United States, it must contain at least 40 percent alcohol by volume (ABV). Some other common botanicals used to make gin include rosemary, coriander, orange, lemon, angelica root, cinnamon, cassia, cardamom, ginger, nutmeg, and ground almonds.

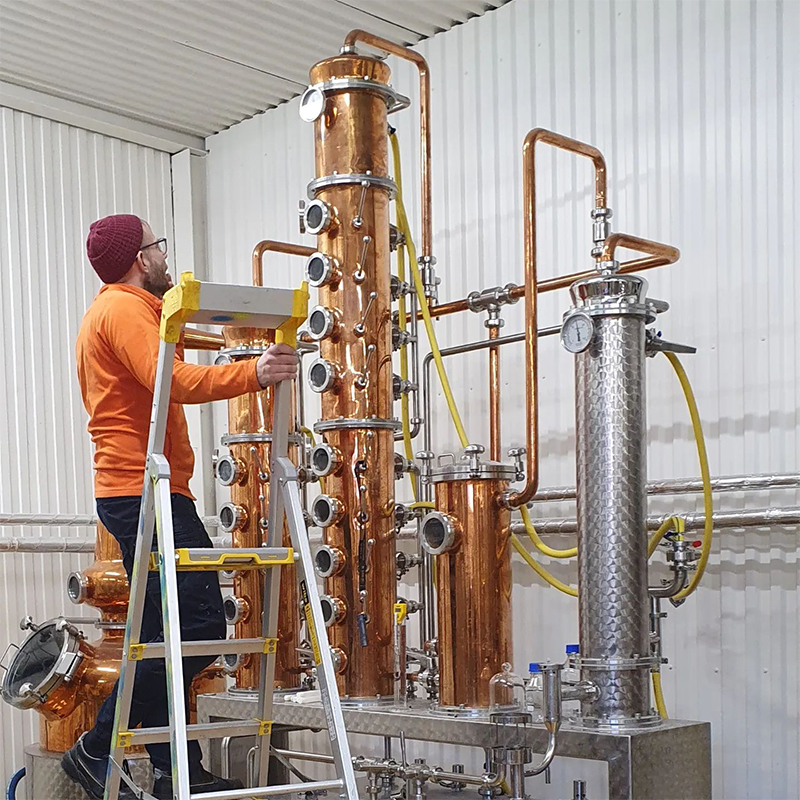
How Is Gin Made?
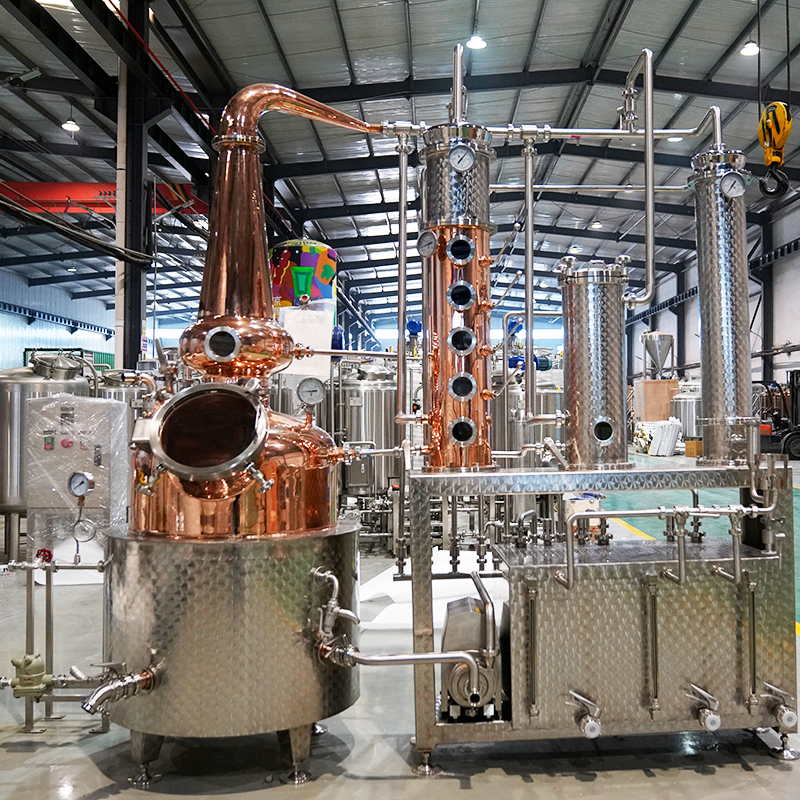
Gin distillers use three methods to purify their ethanol and infuse their botanicals to craft gin.
Steeping
In this approach, the ethanol and botanicals are mixed in a still over a heat source. Depending on the flavor profile that the distiller wishes to achieve, they may remove the botanicals promptly or let them steep for up to 48 hours.
Vapor Infusion
A Carter head still, a modified still with a hanging basket, is used for this technique. This method is similar to steeping and also begins with placing ethanol in a still. The difference is that the botanicals aren’t added directly to the ethanol. Instead, they are placed in a basket that sits just above the alcohol. As steam is created and rises, it releases the essential oils in the botanicals, which then infuse the alcohol with flavor. Typically, this approach is used to create lighter gins.
Vacuum Distillation
This is one of the more modern approaches to distillation,this technique requires a low-pressure vacuum environment. Traditionally, gin is distilled at 78°C/172.4°F. However, vacuum distillation lowers the temperature to a relatively cool 40°C/104°F. This lower temperature means that the botanicals are fully infused and remain more intact. Some distillers combine steeping and vapor infusion, blending the two produced gins together for a compound gin product.The result is a gin with more prominent flavor layers.
Gin Production Wrapped Up
Since gin starts with a neutral base, there is plenty of room to get creative when adding different botanicals.The flavors are further influenced by which distillation method is used. All this combines to create a robust and complex liquor that is great on its own or in classic cocktails. If you’ve been sticking to your usual rum, vodka, or tequila, it may be time to mix things up by trying some different gin brands.