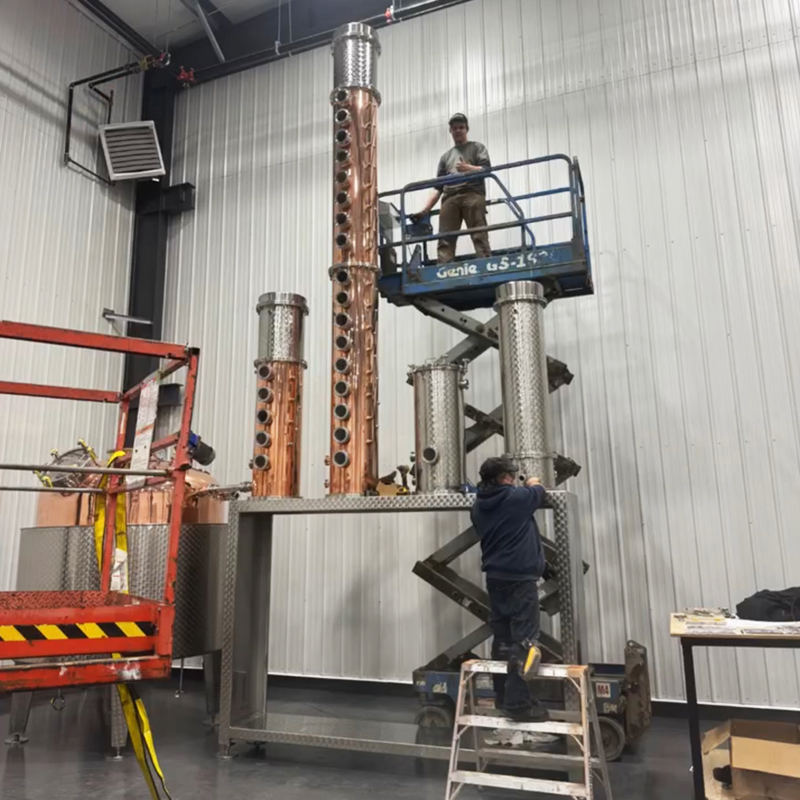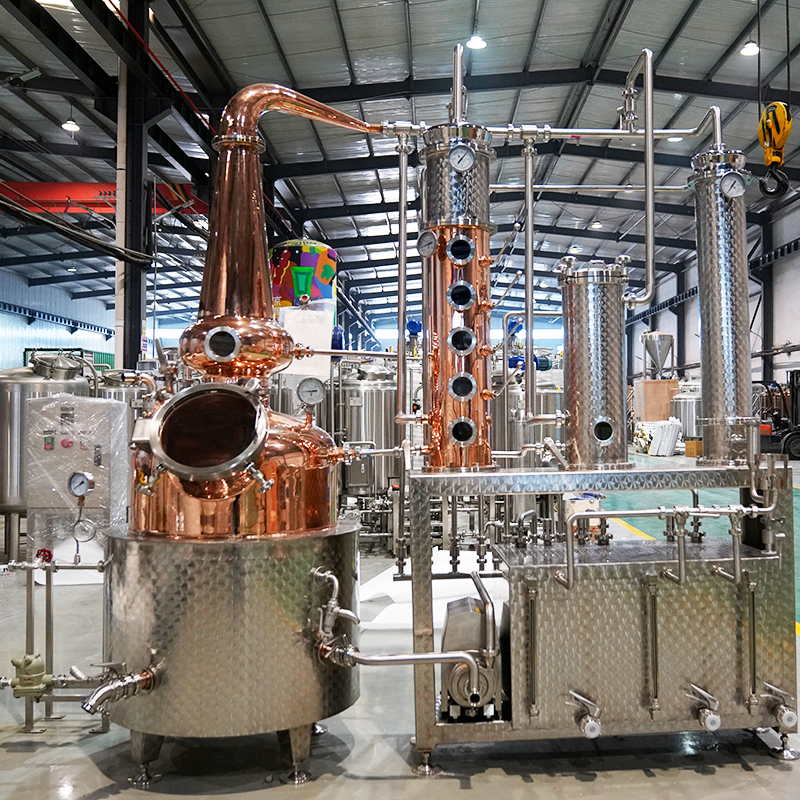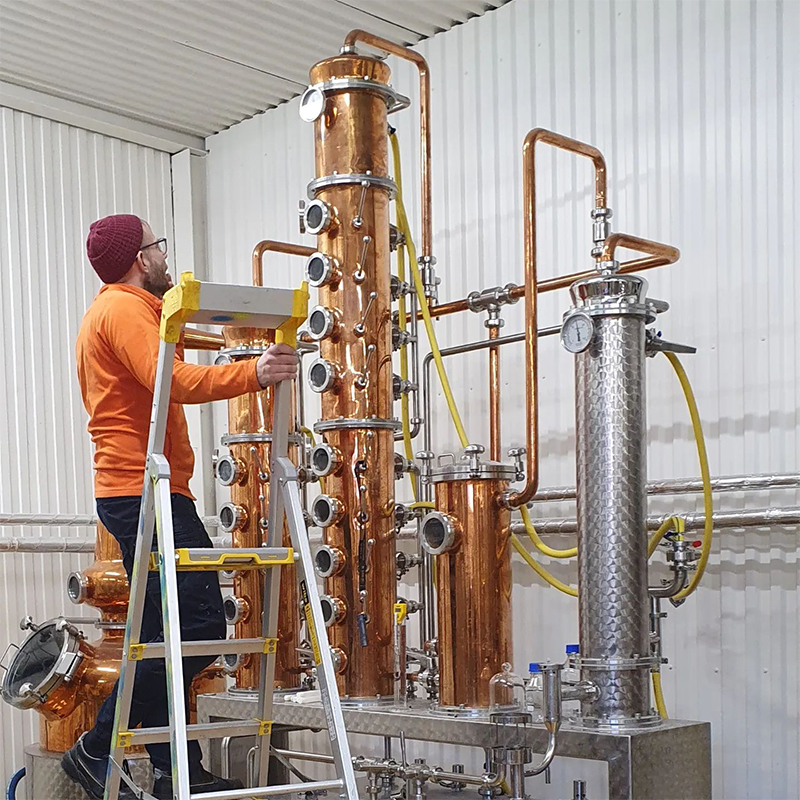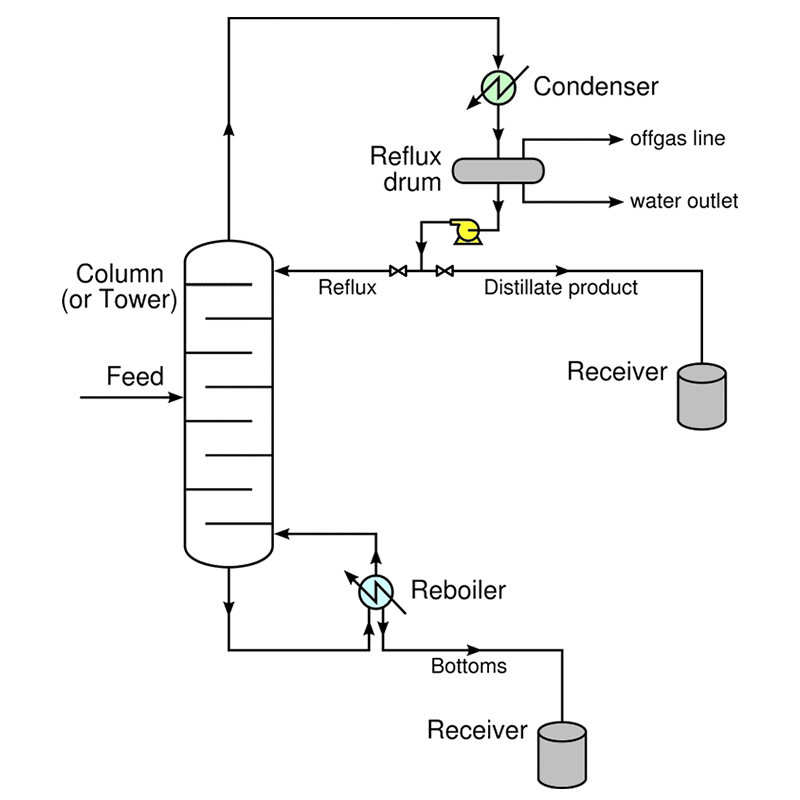
Components of a distillation tower and the distillation process
Distillation columns are critical in separating liquid mixtures into their individual components based on boiling points. By leveraging the principles of heating, vaporization, and condensation, these columns enable the efficient purification of various substances. They are widely used across industries such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and beverage production.
The design and operation of a distillation column vary depending on the type of liquid mixture being processed and the desired product specifications. Here, we’ll explore the components, process, and key types of distillation columns.
Components of a Distillation Column
A distillation column comprises several essential parts, each playing a specific role in heat transfer or matter separation:
Vertical Shell:The main body of the column where liquid separation occurs.Provides structural support for the internal components.
Tower Internals:Includes trays or packing materials that facilitate the separation process by increasing the surface area for vapor-liquid interaction.
Trays: Sieve trays, valve trays, or bubble cap trays ensure effective vapor-liquid contact.
Packing: Can be random or structured, designed to enhance mass transfer efficiency.
Reboiler:Located at the bottom of the column, it provides the heat necessary to vaporize the liquid mixture.
Condenser:Positioned at the top, it cools the rising vapor, condensing it back into liquid form.
Reflux Drum:Collects the condensed liquid from the condenser.
Allows some of the liquid to be recycled back into the column to improve separation efficiency.

The Distillation Process
The operation of a distillation column follows these key steps:
Feed Introduction:The liquid mixture is introduced into the column through a feed line, typically near the middle of the column.
Heating and Vaporization:The reboiler heats the mixture, causing the more volatile components to vaporize.
Vapor-Liquid Interaction:The vapor rises through the column and comes into contact with the descending liquid.
This interaction, which occurs on trays or packing, promotes the transfer of volatile components to the vapor phase and less volatile components to the liquid phase.
Separation:The more volatile components continue to rise, eventually leaving the column through the condenser as a purified liquid product called the distillate.The less volatile components exit the column from the bottom as residue.
Distillation columns are indispensable tools in separating and purifying liquid mixtures. Their efficiency depends on their design, internal components, and operational parameters. Understanding the functionality and applications of different types of columns helps industries optimize processes and achieve desired product quality.Whether for producing high-purity chemicals, refining petroleum, or crafting spirits, the right distillation column ensures consistent, efficient, and precise separation.








